|
|||||||
| Ссылки сообщества |
| Изображения и альбомы |
| Пользователи |
| Поиск по форуму |
| Поиск по метке |
| Расширенный поиск |
| Найти все сообщения с благодарностями |
| Поиск по дневникам |
| Расширенный поиск |
| К странице... |
|
|
Опции темы | Опции просмотра |
|
|
Язык оригинала: Русский #5 |
|
Авторитет
Регистрация: 25.10.2008
Адрес: Киев
Сообщений: 825
Спасибо: 1,587
Поблагодарили 2,452 раз(а) в 384 сообщениях
Записей в дневнике: 2
Репутация: 3846
|
A brief overview of the history of art in Mesoamerica. (Excerpt from the introduction to the album "The Art of Ancient Mexico" M. 1962, author - I. Golomshtok.) ... Only at the end of XIX century there began a systematic study ancient Mexican culture. As a result of the excavation of the ground reappeared works of Indian masters. Initially, the regarded as primitive idols or funny freaks: from the point of European art of the XIX century, the ideal which has continued remain calm beauty of ancient Greece, the peculiar form Mexican art seemed crude and imperfect. Only Now it begins to reveal to us the richness of its forms, all unique originality of his artistic language and content.
Читать дальше...
History of ancient Mexico are poorly understood. We know much more about pharaohs of ancient Egypt, of the great masters of ancient Greece than of builders of the giant pyramids of Mexico, the creators of the magnificent monuments of sculpture and painting, lived in the same time as Giotto, Andrei Rublev and Durer. Mexican civilization is one of the oldest on earth. Getting lost in the depths of millennia, and the end refers to the relatively recently - in 1521, when the Spaniards destroyed great city Tenochtitlan - the capital of the powerful state of the Aztecs. It is believed that the first settlers appeared on the territory of Mexico approximately twenty-five thousand years ago. ... ancient images of people in the Mexican art are clearly pronounced Mongoloid features, which confirms the Asian origin American Indians. The most ancient monuments of Mexican culture date from the II millennium BC. e. In those remote times, Indian tribes were still at primitive stage of development. Some tribal settlements were combined centralized system of government, and scattered people's notions about the universe has not yet resulted in a coherent religious system. The art of ancient agricultural tribes bears the imprint ease their way of life and world view. From this time until we survived numerous clay figurines depicting women. Squat, with a large head and short trunk, they then sit in a relaxed poses, then, raising his hands and threw back his head, lay eggs in the fast paced dance then keep children or dogs, then wept bitterly, his face in his hands. Some of them are depicted with exaggerated big hips and bellies; obviously they embodied the idea of the fertility of the land, which then entirely depended on the existence of people. Other figures are depicted with two heads. Perhaps ancient masters have sought such a rather naive way to pass the motion man, maybe they portray here struck their imagination and their inexplicable phenomenon - the birth of twins, the exact purpose of these figures is unknown. Creative artists who created them have not been constrained by tight outside the religious system. They did not know the canons, the source creativity serve the surrounding reality. These clay figures is striking how the vitality of postures and movements ny, the naive charm of spontaneity in the transfer of diverse GOVERNMENTAL specific details: coquettish haircuts, coloring, transmission, obviously, the real colors, which covered the body of ancient indey - particle. They are scattered like bright sparks of life. In VI century BC. e. Gulf Coast blooms Olmec culture of the people. That people knew the higher forms of ob - substantially organization. Olmecs lived in cities, they gain writing, they watched the movements of the planets and on the basis of these Observations made his calendar, which, over time, pre - gateway to a better system of chronology than the Gregorian, sky calendar, adopted in medieval Europe. Their presentation of the world are drawn into a coherent system of religious attitudes, in which Roy took great jaguar cult. In the religion of the Olmec-warehouses vayutsya features, which subsequently became characteristic of the religion-pain The vast majority of peoples of ancient Mexico: the presentation of life and death as two equal footing in the general circulation of nature, pre - submission of the duality of each phenomenon and the universe as a whole In honor of their gods, Olmec erected huge pyramids, employees giant pedestal for being at the tops of their temples. Art Olmec obeys the expression of religious ideas. The wealth of vital parts of art replaces the previous period, Xia therein strict laconic artistic means, and no longer soft clay, and hard jade, basalt, and diorite embody the image the very essence of human creation, as understood its ancient masters. Produced a strict canon of the image. Scowling forehead, widely apart, as if staring into infinity eyes half open - ty as if in mortal agony, making the last gasp of mouth -- These features were sealed in small funerary masks and a giant - skih stone heads, which reach heights of 3 meters and weight -- 18 tons. These images have a certain cult character. They, obviously, embodies the idea of indissoluble unity of life and Smer - ti-the basic idea of the Mexican religion. Typical for all iso - brazheny particular trapezoidal shape of the eyes and mouth, reminding yuschie eyes and mouth of a jaguar, and symbolically link them to the cult of terrible ruler of life and death. Olmec culture ceased in I century BC. AD., never opened us the mystery of his birth and causes of death. From it have their origin many later classical culture of ancient Mexico. However drevnemeksikanskaya culture is not a single whole. On the vast territory of Mexico for two thousand years liv - lo many different tribes, separated from each other trudnoproho - sary jungles, mountain ranges and deserts. Some of the tribes - voevyvali others perceive their culture and through it created own, others have evolved independently. So, on the Pacific coast in ancient times there was distinctive culture, known as "Western culture", or point - her, culture of the West Coast, which lasted until at - of the Spaniards in America. Little is known about the tribes that have established great monuments of this culture. It was not begotten. Art of the West is divided into two opposing styles of products. In some only roughly mapped out the basic forms of human and animals. In brute force and straightforward simplicity of these fi - Gur evident desire of their creators to identify constructive noun - tions image - his "skeleton". Another group included - chaet a huge number of images of soldiers, Gorbunov, acrobats, childbirth, etc., are rendered with surprising realism and artistic freedom. These are different in character pa - specimen were found in different geographical centers, perhaps they created in different chronological periods. To the east of the dissemination of Western culture on pobe - rezhe Pacific in the V century BC. e. begins to develop Culture Zapotec, which was also destroyed by the Spaniards. Zapotec were warlike people. Important role in their lives played the high priest, and it is largely subordinate to the administration of religious obrya - Dov. Have survived many Zapotec funerary urns, in which They buried the ashes of the dead. These boxes are made most often in the form of sit - ing people in wealthy clothes. Decorations are closely intertwined, melt them with religious symbols and create a fantastic fantastically curvy shape, sometimes resembling exotic the plants Nia tropical jungle that surrounded this nation. The art of self - water stains we associate with the art of ancient India and China. Direct descendants of the Olmec were Teotihuacan (200 -- 800 years. Mr. e.). At 40 kilometers from Mexico City lie the ruins of hyper - gantskogo city of Teotihuacan, and still occupy space eye - Lo 17 square kilometers. In this city there was no residential buildings, he never lived people: he was devoted to the gods and consisted of hra - mov and religious buildings, above which rose two giant - skie shestidesyatimetrovaya pyramid-pyramid of the sun and a little inferior to it by the size of the pyramid of the moon. In sculpture Teotihuacan revives the spirit of stern Olmec art. The same expression predsmert - Noah agony, that of the Olmec sculpture we see in the funeral masks created teotiuakenskimi sculptors, the same stern varnish - nism, synthesis and strict geometrizm distinguishes each made - tion of their art, which has a pronounced cult character. The Gulf Coast after the disappearance of this ol - mekskoy culture emerged and developed a culture of several tribes. In the north of the area about 200 years BC. e. begins to develop - Xia Huasteca culture. Huastec people were brave warriors and skilled farmers. Many times they have committed conquest against neighboring tribes, and until the arrival of the Spaniards defended their independence from the powerful state of the Aztecs. Their Religion and their art were as simple and harsh as a dangerous life of an Indian warrior. Sculpture Shilonites - goddess of mature maize (Huasteca) - is sitting in the typical Indian clothes and ornaments. In a block of stone sculptor sets out a basic WIDE outlines of human figures and details of clothing. Powerful plastic heavy volumes, severe expressive simplified forms of transforma - They provide a benefit in this picture stood motionless idol, who served the object of worship. The stark power and monumentality of the images constitute the basic quality of art Huasteca. Another character is culture Totonacs, which has spread on the Gulf Coast south of uastekskoy cul - ry and developed here with the VII to XII century BC. e. Their art is different is developed and a large variety of forms, more difficult - Stu and refined aesthetic principles, sometimes approaching to the norms of European art in the interpretation of the image rights. Striking consummate skill of these artists communicate complex angles of the body, a wide amplitude of the internal condition of man, from Homeric laughter masked actors and to the expression of senile discontent. Mixteco, inhabited the central part of Mexico in the IX - XVI centuries BC. e. were superb jewelers. They created ceramic cal products, ornaments of gold and rock crystal and even arch - tekturnye structures differ refinement of proportions, rich - stvom ornaments, jewelry subtlety processing. Great builders were Toltecs - tribe, which appeared in the IX century BC. e. in the central part of the country, has created this high cul - round, but was defeated by the neighboring tribes and forced intersection pour on the Yucatan Peninsula, where their culture was absorbed into civilization tion mayev. Culture mayev is undoubtedly the highest of all the ancient their American cultures. During its more than a thousand development - culture emerged in the IV century BC. e. and lasted more Some time after the arrival of the Spaniards in America - Mai reached high degree of social organization. They bloom astro - miya, mathematics, medicine, literature, they are building a large city life which plays a major role, not only spiritual, but the secular aristocracy. Art mayev stands out for its realism of the art of ancient American tribes. Along with the sci - Skim images of gods and complex symbols are part of the meeting - ARE pictures of priests, warriors, ordinary people, damaging life - nennoy truthfulness in the transfer of the anatomy of the human body movements and clearly defined national facial features. Open recently and have become famous painting of the sanctuary Bonampak brought us episodes everyday life of the people; elaborate preparations for a military campaign, a fierce battle with the enemies, a magnificent celebration of the victory. In imagery human repeated the same type -- thin, highly elongated to the bottom face, long thin figure nose, small mouth with energetic, large oblong eyes, one and the same expression of restraint, the aristocratic nobility and inner strength. Obviously they very accurately re - given not only the racial traits of the people, but also his character. And this - hour, after several centuries of severe repression and Enforced Noah evropezatsii in remote areas of Mexico, where among tropical forest rose once civilization mayev, you can meet these Indians - tall, strong, brave, served as a fashion - sentatives of the ancient masters. The last and most powerful civilization of ancient Meck - shiki was State Aztecs. In the XIII century, this warlike nation motion nulsya from the north of the country in search of land, favorable for farming. This campaign lasted for a long time, until finally, on the shore of Lake Texcoco Aztec not see an eagle tearing a serpent, that the prediction of their gods was sign of the promised land (Picture eagle tearing a serpent, and now included in the national emblem of Mexico.) Here, in place of the present capital Mexico, in 1325 founded the city of Tenochtitlan, the population and area which, according to the Spaniards who saw it exceeded any city of medieval Europe. In an amazingly short time - less than than 200 years - the Aztecs created a powerful military state, subjugate all the neighboring tribes, and have achieved great success science, art and culture. Art of the Aztecs bears imprint of their religion - the grim and brutal of all religions, ancient it America. They have developed and brought to completion common to MERGE Caen religions the idea of the universe, as the unity and balance of the two opposites, life and death. Violation of equilibrium inter - do them on the submissions of the Aztecs, leads to a cosmic catastrophe threatening the existence of people and their need to avoid infinite nechnye human sacrifice. This idea was shaped in - ploschenie a terrible image of the Aztec the goddess of life and death Coatlicue with a skull for a head, in clothes of the serpent, and two pairs hands, giving and consuming lives. Ancient Mexicans were closely acquainted with death. Death awaited rights in the jungle, teeming with wild beasts, it is the mixture tala entire peoples river flooding and volcanic eruptions, blazing rays of the sun, she burned the crops of maize and transformed in the desert CEE - tuschie city. Ancient Indians did not close her eyes, they attempt - lis comprehend it. Perhaps, in the minds and in religious ceremonies or one of another nation's death has not been in such a place of honor, as the Aztec, and throughout the world of art is difficult to find a more expressive - WIDE images of her image than the Aztec gods Shipe-Toteka and Coatlicue or "head of the deceased", in which almost naturalistic transfer "Physiology" of death is combined with its tragic pathos. Images of people in Aztec sculpture da HN is still frozen in the poses and gestures of their hands strictly fixed, faces like masks. The eyes are either deprived pupils, or inkrustirova - HN colored stones and pearls, and this illusion of living vzglya - yes to a deathly gray, very generalized rock surface mask creates a strange effect: the eyes as it concentrated in itself all the great tension and inner life in contrast with more fixed, frozen, lifeless perceived faces and figures of these people. Dead and alive closely intertwined in these sculptures, stands in a stable equilibrium and deter - lyaet their dark, intense, detached from all the random and pre - walking, from all the accretions of daily life art image. That is - in very general terms - a picture of the ancient MEX - Sican art, is a complex conglomerate of WHO - nick, endangered, and mutually destroy each other cultures, which are now an archaeological map of Meck - shiki has about eleven thousand. In this art there is no single line of development from lower to higher, it affects the very inhomogeneous geneity goals and challenges faced by artists of various films, Man and historical periods, the extraordinary variety of forms, decision ny and stylistic principles. Yet we can speak about deter - shortages in the unity of the ancient Mexican art, about the specifics, which distinguishes it from other known ancient cultures - Antic - Noah Greece, Egypt, etc. Mexican art emerged and developed in the conditions of first - bytno communal system in the transition period from the middle stage of barbarian STVA to death. This stage of development of mankind does not yet know the full separation of different spheres of human practical activity. Nau - some more closely connected with religion, and of the universe, expounding lis if not in literary works, not in philosophical and theological - cal treatises, and translated into art, especially in sculpture, painting and architecture. Will be yet in the Olmec writing, wore a pictographic, ie, descriptive nature. Story about a particular event, provide an account of Cheredova - tion of symbolic images of the participants, their actions, of the objects, Comrade environment in which it occurred. Many ancient monuments Mexican culture it is almost impossible to discern where it ends pictographic presentation of scientific and religious ideas the world and begins his aesthetic comprehension, ie, the probation - stvo. All this is in them in close unity, as an indissoluble synthesis. Thus, the image of the god of the sun , the ancient mayev represents in fact, a complex icon. Overhead god rise several - Kimi tiers images of birds, animals and humans that are symbolic lyse various stages of creation of the world that deity, his face decked out symbols of fire, water and land, in the image introduced the so - the signs of numbers, months, etc. Zapotec funerary urns equipped with the powerful attributes of the god Tlaloc (blinkers on chap - Zech), jaguar (D-shaped mouth) and bat (big ears), con - unlinked to the cult of the dead. However, the picture is not limited to mechanical Český enumeration of these characters and attributes. Their combination make it possible to lyaet achieve high expressiveness plastic forms: snarled - shiysya mouth with protruding fangs, sunken, covered with wrinkles cheeks, sunken eyes, the dark rusty-red color transfer here sense of death as a terrible and inevitable force. Ancient sculptor - Tori created in these works, the whole poem about life and death, about God, about the universe, in which the "text" and "illustration" merged in a single Mr. image. Their content is disclosed and through the visual perception * ment of artistic form in general, and as if by reading it individual elements. Not without reason in writing of the ancient concept mayev "Write" and "paint" refers to one and the same sign. Old sources reported as American Indians, who did not know before - Mashnaya animals, except dogs, performing their role thrust - angular forces, first depicted struck their imagination horse. Progress thinking they were at the same time something like this: a horse pulls the load, so it looks like a dog, but it is big as deer - and Indian artists depicted her with a head of a dog, but with - gami and ears of a deer, coyote tail, etc., expressed in these characters, his metaphors of the horse, not as an individual concept, as well as some general category .- Along with this kind of symbolic images, switching - repentant of pictorial writing, the art of different MEX - Sican tribes found images which are of pronounced realistic features. In the culture of the West Coast is represented, Nia players in the ball, giving birth, a hunchback, little fat dogs, y Totonacs-figure seated men and women have mayev-sculptures of priests and warriors, the Aztec images of coyotes, snakes, etc. These product of Denia demonstrate excellent knowledge of their authors anatomy humans and animals, about the ability to communicate complex movements and internal even if domestic status of people. However, the significance of such images for ancient Indians was not only that. Realistic form pre - meta-whether man or animal - they have subordinated the expression main, seemed the main idea. A typical example is the figure of a warrior with a sling, referring - converging to Western culture. Truncated body, which might emphasizes barrel armor, and thick short legs create a firm support for the strike sling, which compress the hands of warriors, on. From under the helmet pulled down low is directed to the point of impact pristal - HYDRATED opinion, and even moving the lips can feel the internal tension concentrated on one goal. The image of strength, focusing on one act - impact - has created a master here, subjecting the identification This idea forms the human body. The idea of a man's strength is expressed here not only through anatomical mechanism of the body, as in drevnegre - Ceska culture, but also through the plastic expression of individual form elements - volume, movement, composition scheme. One - However, despite underlined the dynamics of gesture and a sharp turn, motion zhenie figure seems constrained, frozen in some eternal immobility. It seems that the body of a soldier never unfold for impact. Before us is not the image of a specific soldier in front of specific nym enemy, but some action, which is demonstrated by this product of stipulated time, having, apparently, a cult character. The strength and movement of striking an enemy soldier, captured in sculpture, acquired for the ancient Indian values tion spells, a weapon against the enemy. Despite the high - cue level of development of Mexican art, we are dealing here, obviously, with the stage of creative thinking, when the image human, animal or a certain action magically bind - elk with their actually existing prototypes. Thus, even primitive master Altamira cave paintings in France, depicting the wall bi - zone, believed that he thereby acquires a mysterious power over animals, helping in the hunt for him. Representations of the ancient Mex - Kantsev of the world have become much more complex compared to the way of thinking tion of the primitive artist, but maintained, nevertheless, his magicians, ical basis. -- Many monuments of art of different cultures of ancient Mexico affects the accuracy of the transfer of mental states rights, it seemed incompatible with the common conditional nature of the art. In Pla stick body and mimic the person passed the ancient masters such complex manifestations of the human psyche, as fatigue, laughter, absorption in themselves, fear, ecstasy or agony, etc. To the best examples of Mexican sculptures include fi - guru sitting bound captive. When traversing circular sculptures are in front of us all new perspectives, revealing state of deep despair, persecuted and fear of the vanquished before the winner, looking sullen eyes, bent low, sunken head on his knees, twisted and bound his hands behind his back, strained, as if shrunk into a ball shape ... Emotional expression - proximately here is that you do not notice the imbalances of the body - the hyper - booty bottom of the figure, an unnaturally large head, nepropor - tional small hands. The same can be said about the magnificent vessel in the form of a tired man - ranks, in an image which passed the state of deep grief or extreme fatigue in the modern sense of these concepts. However, one can hardly consider this kind of image as captured in stone psychological studies of individual living through - ny person. Looking through thousands of similar images in Mexicans skom art, we find in them only a few strictly determined lennyh and well-documented states of the human soul, almost without changes in moving from sculpture to sculpture. So in art Totonacs repeatedly vary one and the same type image rights. This female figurines, which cross-legged and putting his hands on his knees, sitting in stationary positions. Their nepropor - tional large head slightly raised, mouths half open, frozen - shy gaze directed at infinity. Imprint detachment from all earthly things, deep in himself lying on these, as if in a trance, motionless figure, somewhat resembling the image bud - dy in the art of India. What is the meaning of these images, just repeating the same state of mind of man? The explanation of this should be sought in the way of life of ancient Indians in their rites and representations, in the very nature of their thinking. We know what role in the lives of the people on the stage of development played religious ideas. Powerful, fierce deity, as approved, gave the myths, deciding the fate of people dictating to a priest. Some Mexican tribal chief priest at certain times climbed to the top of the pyramid, where he offered sacrifices to the gods and fell a trance state in which the predicted fate of the tribe. Sometimes these function was performed by priestesses. The very state of trance, in which the priest contact with the deity, was considered so sacred. Its something evident, and recorded by ancient masters in sculpture as a kind of cul - tovuyu category rather than individual human experiences. We have already mentioned on the expression of agony in The image - zhenii people from the Olmec and Teotihuacan, which embodies "the idea is one - STVA life and death, as two equal footing of the universe. Like - WIDE examples could and continue. In whatever capacity did not depict the ancient masters of the people, their person - always just a mask, they express only a definite HYDRATED type of internal state, not associated with individual re - ities, and which has, obviously, a cult or ritual significance. In that distant period of history man has not yet realized its place in the sun, he had not yet conquered the forces of nature and felt its full dependence on these forces. Image Rights as an independent value - beauty of his body and significant ARRANGEMENTS his being, his inner life and personal qualities - soil - ty has not found another place in this art. It is subordinated to other goals and this determines its specificity. The reality is reflected it refracted through the prism of religious ideas. Con - its specific image, despite his sometimes extraordinary life reliability is always a personification of a certain pony - ment, the embodiment of people's ideas about the world, making it in character. Realism nemeksikanskogo ancient art has such edu - Thus, the historically limited. This magical, or symbolic realism, naturally folded, shiysya in a certain socio-historical environment. Many centuries separates us from the creation of monuments MERGE Kan art. With the collapse of ancient civilizations have disappeared for us and the ideological premises, which were the main drivers creativity of its artists. Swords Spanish conquistadors had interrupts Wang's centuries-old line of development, and now only numerically - nym ancient manuscripts kept in various museums around the world, pa meager reported to have taken the first Mexican land Europeans observe the life of ancient tribes, scientists can only recover fragmented and very approximate picture of the spiritual life of the people. Yes, and what little is known about the ideological assumptions Mexican art, the worldview of the ancient Indians, on their re - Lygia, with its bloody rites, human sacrifice and the deification of abstract concepts - is infinitely far from the restored acceptance of the world of modern man. Yet the ancient art preserved for us the great power of artistic influence. The stark image of masculinity Aztec eagle warrior or refined nobility of the head of the god of corn mayev, dramatic expressiveness of the Olmec and teotiuakanskih immersive ballroom masks or a whole symphony of laughter in Totonacan masked act - ditch-all before us in such an artistic interpretation of habilitation as a sink for all the minor details, and at first plan serves only thing that helps reveal the general idea of the product of Denia. The great degree of generality that converts times The image - zhenie in character, but never deaden the reliability, -- One of the major stylistic principles of this art. Different in nature monuments, ranging from the giant Olmec - skih heads and the finest jewelry Mixtec, contain more one general for the Mexican art quality - the monumental, ie, the ability to identify the main phenomenon is not portrayed in a sub - robnoe listing of individual parts and particulars, and through the plastic form, the ratio of the volume, rhythm, lines, etc. Even the most apparently would at first sight "genre" scenes are devoid of elements byto - vizma and narrative. Thus, frequently occurring in this iskusst - ve image of mothers, for all times of physiological accuracy the transfer of its state has a value not a story about an individual event of human existence, and carries the meaning of critical act of nature: the sacrament of a new life. This art involves not mathematically perfect exported cultural property, sured proportions, not soothing harmony and beauty, as, say, art of the ancient Greeks, but by force of expression, enhanced expression, tions of the artistic image. The history of art of ancient Mexico seems rife neob - yasnimymi seemingly contradictory. Ancient Indians of the User's valis only stone tools, they did not know the wheel, draft animals, and erected magnificent pyramids, temples and sacred cities, they did not know the potter's wheel, but the perfection of their forms of ceramics not inferior to the ancient Greek vases, they are not used metals in the quality - stve tools, and their jewelry, gold jewelry to the present day remain high specimens of applied art. This histori - sky paradox can be explained only by the enormous role Art played in the lives of the people at this stage of his public development. Art embody the most important representations of people the world. It was for the ancient Mexicans and science, and religion, and there - terature, and script, and an ornament of life, and it is therefore way, the focus of all spiritual life of the people. This, obviously, and reality - LOS reason that in Mexico, in the era of the Stone Age have been capacity - HN architecture, sculpture, painting and applied art, is - schiesya one of the peaks in the overall development of human culture. Вложение 130795Вложение 130805 God Art Shochipilli. (culture of the Aztecs) Вложение 130815Вложение 130835 The head of an eagle warrior. Coagulated snake (Aztecs) Вложение 130825 A warrior with a sling (Culture of the West) |
|
|

|
| Меню пользователя Art-lover |
| Посмотреть профиль |
| Отправить личное сообщение для Art-lover |
| Найти ещё сообщения от Art-lover |
| Читать дневник |
| Метки |
ancient Mexico, the art of South America 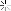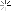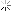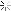 |
| Опции просмотра |
 Линейный вид Линейный вид |
 Комбинированный вид Комбинированный вид |
 Древовидный вид Древовидный вид |
|
|
 Похожие темы
Похожие темы
|
||||
| Тема | Автор | Разделы | Ответов | Последние сообщения |
| Art Sets and kinetic art | LCR | Contemporary Art all over the world | 2 | 26.08.2011 09:46 |
|
|
Часовой пояс GMT +3, время: 14:26.
Powered by vBulletin® Version 3.8.3
Copyright ©2000 - 2025, Jelsoft Enterprises Ltd.
Copyright ©2000 - 2025, Jelsoft Enterprises Ltd.